Did you know that CPUs make a lot of computations? After computations, are they somewhere inside the CPU? New knowledge and understanding of computer technology is beneficial for everyone. Today we will try to answer where the CPU stores its computations.
Where Does the CPU store its Computations?
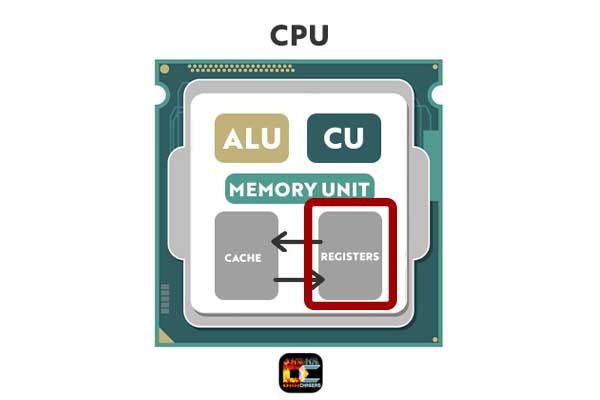
First, CPU computations are stored in registers, because it is much faster memory than cache or RAM memory. Registers usually consist of a small amount of fast storage. These are the fastest areas of memory in a computer, but also the smallest ones.
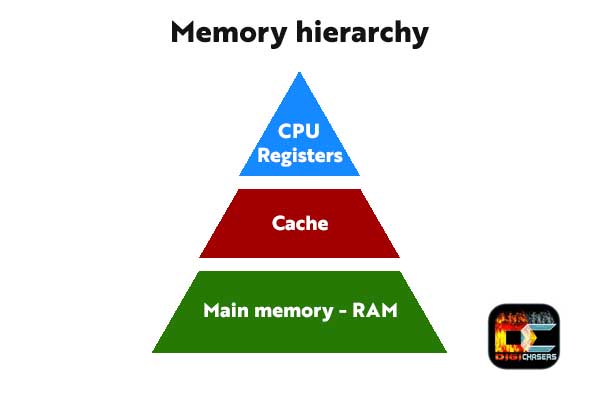
In memory hierarchy, CPU registers almost all the time are on the top. Registers are typically measured by bits it can hold – 8 bit register, 32 bit register or 64 bit register.
As you can see in the graphic picture, in the speed hierarchy first is Registers then Cache.
In CPU there are all types of memory, but in terms of speed and size – registers are the ones that are closest to the actual processing of the CPU.
What do Registers look like?
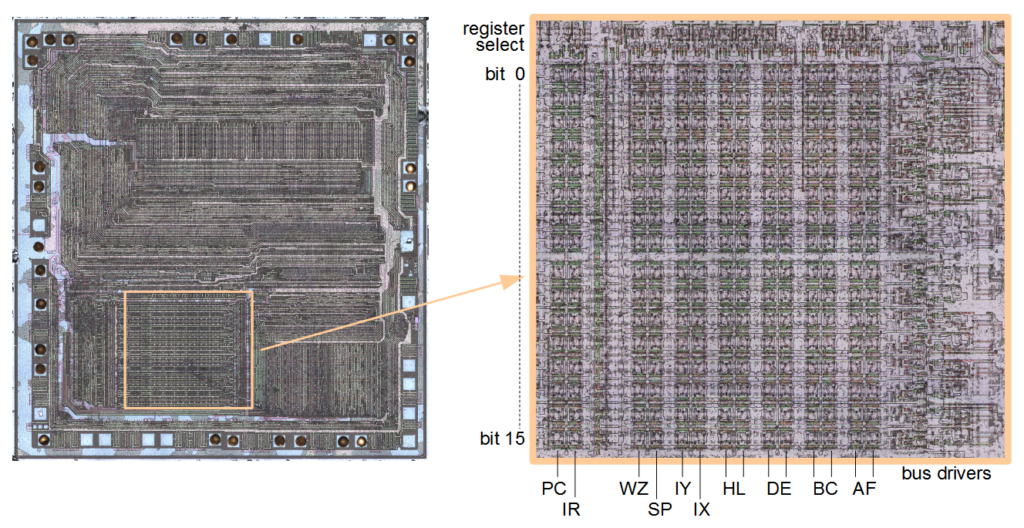
They are so tiny, and are only visible with the help of a microscope.
What is a CPU and what is it’s purpose?

CPU stands for Central processing unit. It is probably the most important part of a computer. CPU are sort of like the brains of your computer. All tasks you do on your computer goes through the CPU, which makes it an essential part of every PC.
On the market are two big manufacturers of CPU – Intel and AMD. Both manufacturers build CPUs that do the same thing – they process information and encode it as ones and zeros at incredibly fast speeds.
The CPU fits into motherboard and the motherboard allows all the components in the pewter to connect to each other.
How a CPU works?
Inside the CPU we have – Control Unit and Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU). Control unit, is the main component that controls what happens inside the CPU. The Control Unit receives its orders from RAM in the form of an instruction, and then breaks that instruction down into specific commands for the other components.
One of the most important component is arithmetic logic unit (ALU). When ALU sends the output to the register. The ALU is what performs all mathematical operations inside the CPU such as addition and subtraction.
A processor register is a very simple component, whose only job is to store a number temporarily. The register is used to quickly accept, store, and transfer data and instructions that are being used immediately by the CPU. Register size determines how much information it can be stored.
Types of CPU Registers
- Temporary register – Holds Temporary data.
- Data register – Holds memory operand.
- Address Register – Holds address for memory.
- Program Counter – Holds address of instruction.
- Instruction Register – holds instruction code.
- Accumulator – Processor register.
- Input register – Holds input character.
- Output register – Holds output character.
What is Cache Memory?
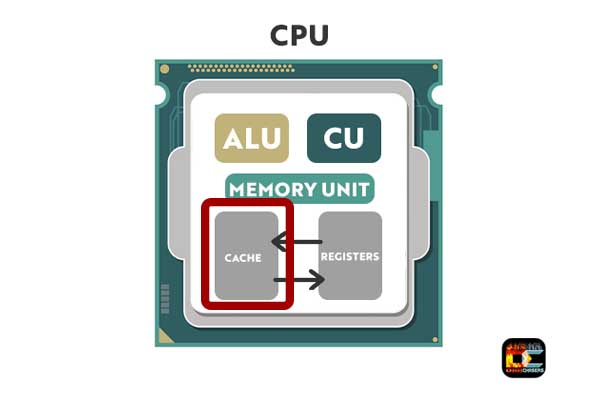
CPU cache, or in other words SRAM is a lot faster than regular RAM and also much more expensive. The CPU cache is the CPU’s internal memory, and its job is to store copies of data.
The CPU Cache main job is to hold common data (instructions), which it intends to use several times. And when the CPU needs some information, firstly it checks the CPU Cache memory. If there is no such data, then it goes to RAM memory, which is much slower compared to cache memory. CPU Cache does not make his computations, it stores them for some time.
CPU cache is an area of memory on the CPU that is used to store the next instructions that need to be executed. Usually you get level 1 cache, level 2 cache and registers.
Author Recommended Reads:
- How to Undervolt Your CPU & GPU – Complete Guide (Safe)
- Thermal Paste on CPU Pins / EASY FIX
- CPU Stuck to Cooler / EASY FIX
- Why are Noctua fans brown? We asked Noctua.
If you have questions, feel free to ask them in the comments section. We hope that this article was helpful to you.

