Hello, everyone who uses a computer has heard of the concepts – Latency and Bandwidth. But do you know what these terms mean? Is it worth comparing Latency VS Bandwidth?
Latency VS Bandwidth
Latency and bandwidth are two different things. Latency is the amount of time during the first signal reaches the target, and bandwidth is the data traffic that can travel at the same time. Latency is one of the primary indicators of network performance quality, which means if your internet latency is big, that means your provider can use old or weak signal technologies.
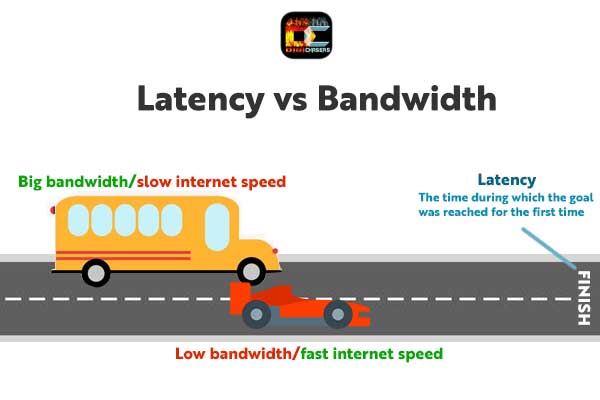
There is a great comparison: a bus can move many people but slowly (it has great bandwidth, but slow internet speed), formula one car can move one person really fast (low bandwidth but high internet speed). If the goal is to move one person – formula one car always wins.
Faster Bandwidth means lower Ping?
PING is a unit used to measure latency. As you already understand, faster bandwidth does not mean lower PING, in case you don’t have extremely small bandwidth. Bandwidth is a measure of capacity.
What is Bandwidth?

Bandwidth is is the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted per second. Or in other words Bandwidth is measured as the amount of data that can be transferred from one point to another within a network in a specific amount of time.
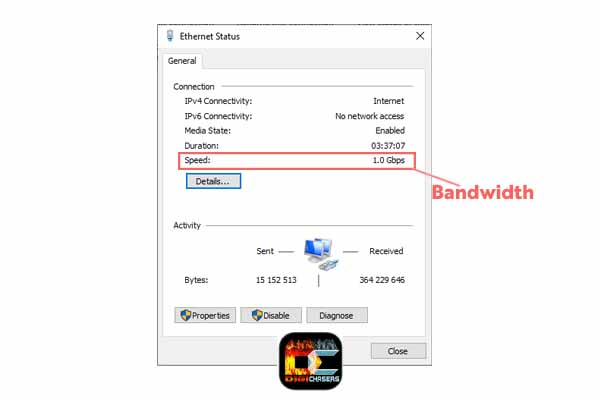
For example, if you have a small diameter pipe, that means that you can run a certain amount of water through the pipe. The Ethernet connection has a bandwidth of 1000 Mbps (download speed 125 megebytes per second). But that doesn’t mean your internet speed is this big, it does mean that your ethernet connection has the ability to transmit that kind of data traffic.
What is Latency?
Latency is the time it takes to complete the stage of the task. If there is only few of bits to move, most of the waiting time is for the first bit. The gap between sending a signal (data) and reaching its destination is Latency.
When data travels across the internet it moves as light in the fiber cables. The time it takes to signal across the atlantic and back is about 0,05 seconds.
So why does it often take so much more time? The extra delay is not just due to time it takes light to travel. There are 3 main problems combined.
Big Latency – Why does this Happen?
No matter how bad it will sound, big latency time often doesn’t depend on me or you. It depends on the big Internet industry.
- The hundreds of junctions in the internet that your data passes through are designed to absorb or buffer your first activity. Unfortunately these buffers have become bloated and due to an oversize they stay full the whole time when date has been transfer.
- Before you can interact with your device and the computer on the other end you need to agree on how to talk to each other.
- Before getting up to speed your computer has to start very slowly and speed upgraduatly. If every rate increases it has to wait until the other end to confirm that the last increase wasn’t too much. This is necessary as the network capacity is shared between users. And it is impossible to know how much traffic other users will send in the next moment.
Author Recommended Reads:
- What are PCIe X1 Slots Used For?
- My IP address looks weird. It is totally normal phenomenon.
- How to Set up a Media Server at Home
If you have questions, feel free to ask them in the comments section. We hope that this article was helpful to you.